Traintastic manual
v0.3.0-master-1565-1c3d48b4
Build 2025-04-25 12:12:15
Preface
This manual provides information about using the Traintastic software to operate a model railway layout. This manual is far from complete, many sections still need to be written. The manual is written along with the development of Traintastic. If you have any questions or sugesstions to improve or extend the manual, please let us know at traintastic.org/contact.
Introduction
The Traintastic model railway automation software consits in two part. The Traintastic server program which controls and operates the layout and the Traintastic client program which visualizes the layout operation. The client can run on the same computer as the server but also on multiple other computers, for larger layout multiple PC's can be used along the layout.
Getting started
This chapter explains the basics of Traintastic and describes the initial steps to get started.
Installation
Installation is different based on the operating system used. Hereafter the instructions for Windows and Linux.
Windows
Installation on Windows is very straight forward. Download the latest release from traintastic.org/download, run the installer and follow the steps below.
Step 1: Windows defender
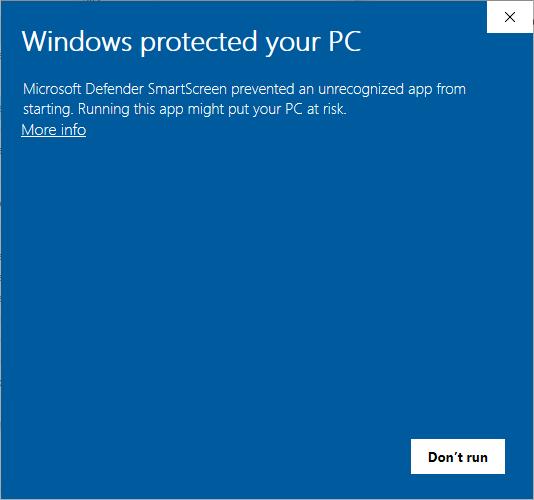
Click More info to show application information.
Step 2: Windows defender
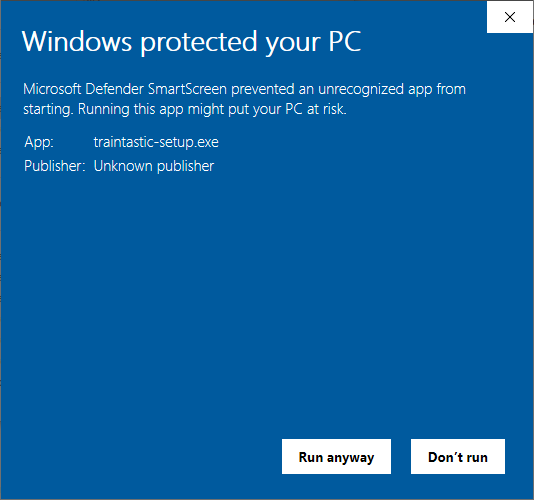
Click Run anyway to start the installer.
Step 3: User Account Control
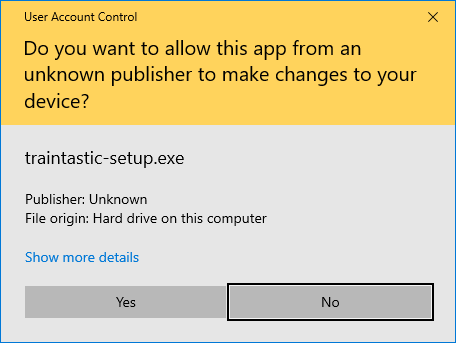
Click Yes to allow running the installer.
Step 4: Select language
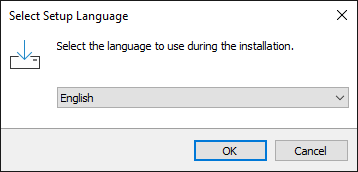
Select language for the installation wizard and click OK.
Step 5: License agreement
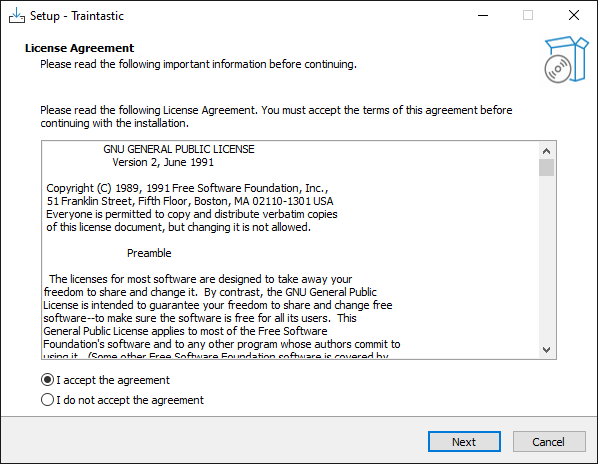
Select I accept the agreement and click Next.
Step 6: Select components
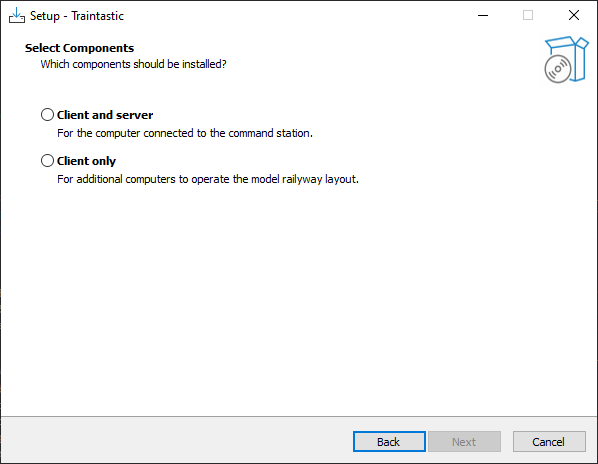
Select Client and Server if this computer will control the layout or select Client only if this computer is used as additional computer to operate the layout. Then click Next.
Step 7: Desktop shortcuts and firewall rules
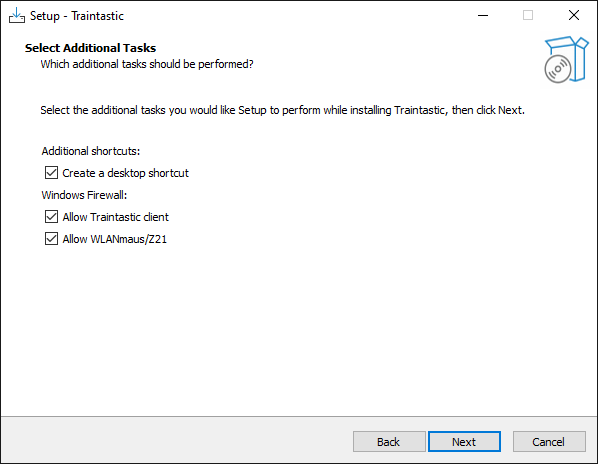
Uncheck Create a desktop shortcut if you don't want desktop shortcuts to start Traintastic. Firewall rules will be added to allow other PC's and device to connect to Traintastic, can be unchecked if not necessary. Then click Next.
Step 8: Ready for installation
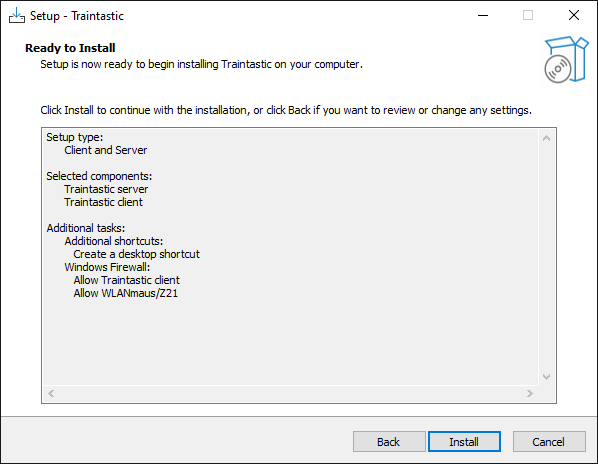
Click Install to start the installation of Traintastic.
Step 9: Installation finished
Click Finish to exit the installer. Installation is now completed.
Linux
Download the latest client and/or server package for your distribution at traintastic.org/download and install is using your graphical package manager or by running sudo dpkg -i package_name.deb in the console.
Starting the server
When running Traintastic, the server should be started first.
Windows
The Traintastic server can be started using the desktop icon (if installed) or by selecting Traintastic ➔ Traintastic server from the Windows start menu. Traintastic server runs as background process, a Traintastic icon will appear in the system tray next to the clock. A Windows notification is displayed when it is running in the background. Traintastic server can be quit by clicking on the Traintastic icon and selecting Quit from the popup menu.
Linux
When installing Traintastic server using a Debian package it is installed as systemd service.
To start the Traintastic server using systemd, open a terminal and run the command:
sudo systemctl start traintastic-server.service
To stop the service, use the command:
sudo systemctl stop traintastic-server.service
Ensure you have the necessary permissions (typically root) to manage systemd services.
Auto start on system boot
To enable Traintastic server to start automatically at boot, run the following command in a terminal:
sudo systemctl enable traintastic-server.service
To disable automatic start at boot, run the following command in a terminal:
sudo systemctl disable traintastic-server.service
Starting the client
When Traintastic server is running the Traintastic client can be started.
Windows: The Traintastic client can be started using the desktop icon (if installed) or by selecting Traintastic ➔ Traintastic client from the Windows start menu.
Linux: To start Traintastic client, open your desktop environment's application launcher, search for "Traintastic Client," and select it from the list.
Connect to the server
When the Traintastic client is started a connect to server dialog will appear. The Traintastic client will automatically search the local network for running Traintastic servers. Usually there is only one Traintastic server running, connect to it by clicking on the Connect button. When successful the dialog will disappear and the main application dialog becomes active.
Main menu

TODO
File menu
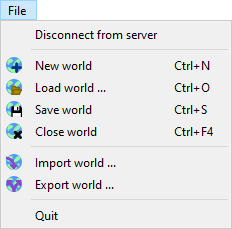
- Connect to server: Connect to a traintastic server.
- Disconnect from server: Disconnect from traintastic server.
- New world: Create a new empty world. If a world is loaded already it will be closed.
- Load world: Load a previously saved world from the server.
- Save world: Save the world at the server, if the world was saved before a backup is made automatically before it is overwritten.
- Close world: Leave the world that is currently loaded.
- Import world: Load a previously exported world into the server. The imported world is not stored on the server until the world is saved.
- Export world: Download a copy of the world from the server. This can be used to make an additional backup or to transfer the world to another system.
- Quit: Quit the application, this does not quit the traintastic server application.
View menu
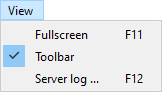
- Full screen: Enable/disable full screen mode.
- Toolbar: Show/hide the toolbar.
- Server log: Show/hide the server message log.
World menu
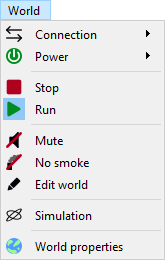
- Connection: Enable/disable communication with hardware interfaces.
- Power: Enable/disable (track) power.
- Stop: Stop all vehicles.
- Run: Allow vehicle to move.
- Mute: Mute all sound effects.
- No smoke: Disable all smoke effects.
- Edit world: Enable/disable world edit mode.
- Simulation Enable/disable world simulation mode.
- World properties: Edit world properties like name and scale etc.
Objects menu
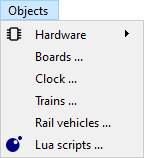
- Boards: Open list of all boards, see board chapter.
- Clock: Open the world clock. (under development)
- Trains: Open list of trains. (under development)
- Rail vehicles: Open list of rail vehicles. (under development)
- Lua scripts: Open list of Lua scripts, see scripting chapter.
Hardware sub menu
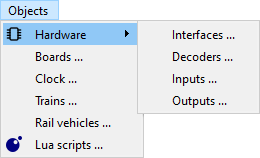
- Interfaces: Open list of all interfaces.
- Decoders: Open list of all decoders.
- Inputs: Open list of all inputs.
- Outputs: Open list of all outputs.
Tools menu
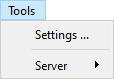
- Settings: Open application settings.
Server sub menu
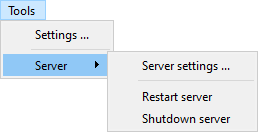
- Server settings: Edit server settings.
- Restart server: Restart server application.
- Shutdown server: Shutdown server application.
Help menu
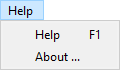
- Help: Open online manual.
- About: Display version and copyright information.
Toolbar
The toolbar contains items that are frequently used when operating the layout. The toolbar can be hidden by selecting View ➔ Toolbar in the main menu.
Online/offline
Toggle world online/offline, this sends a go online or go offline event to all command stations.
Power on/off
Toggle world power, this sends a power on or power off event to all command stations.
 Stop
Stop
Emergency stop all trains.
 Run
Run
Restore last known speed and direction of all trains.
 Mute
Mute
Disable all sound functions, this requires that sound or mute decoder functions are set to the Sound or Mute type, see decoder function function.
 No smoke
No smoke
Disable all smoke generators, this requires that all smoke generator decoder functions are set to the Smoke type, see decoder function function.
Edit mode
Traintastic as a special edit mode, when the world is not in edit mode most settings that define the layout can't be changed. This prevents making accidental changes during layout operation. Changing some settings also also requires the world to be stopped.
The world
The world contains everything that is on the layout, like the command station, trains, signals, turnouts etc. A new world is created by selecting File ➔ New world from the main menu. Existing worlds can be loaded by selecting File ➔ Load world... from the main menu, a dialog will appear with all worlds available on the server.
Setup command station
For operating the layout Traintastic needs to know how to communicate with the command station. To setup the communication with the command station an interface needs to be created. Select from the main menu: Objects ➔ Hardware ➔ Interfaces, a dialog appears which lists all interfaces. The world must be in edit mode in order to create a new interface. To add an interface click the blue plus sign, a menu will appear with different types of interfaces:
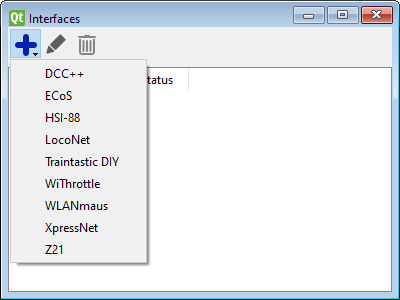
Details about how to setup a specific command station can be found in the supported hardware section. If required multiple interfaces can be added, e.g. an XpressNet interface for controlling the trains, turnouts and signals and a HSI-88 interface for reading feedback sensors.
When the interface is added communication can be enabled by clicking on the toolbar connect button or by selecting World ➔ Connection ➔ Connect form the main menu. Open the server log by pressing F12 hotkey or seleting Vie ➔ Server log from the main menu. If an error occurs while connecting to the interface it will be shown in the server log.
When the connection is made successfully enable the track power using the toolbar button to by selecting World ➔ Power ➔ Power on.
Hardware
TODO
Interfaces
TODO
LocoNet interface
TODO
Trains and vehicles
TODO
Decoder function
Id
TODO
Number
TODO
Name
TODO
Type
Function type:
- On/Off: Indicates a generic on/off function.
- Momentary: Indicates a momentary function, e.g. a horn or bell. The function is automatically disabled after the momentary duration.
- Hold: Indicates a push and hold function. The function is enabled as long as the button is pressed.
- AlwaysOff: Forces a function to be off.
- AlwaysOn: Forces a function to be on.
Function
Function function:
- Generic: Indicates a generic function.
- Light: Indicates the light function, usally F0 or FL.
- Sound: Indicates the sound function. All sound functions are temporary disabled as long as the world mute option is active. If the decoder has a mute function, the mute function is prefered.
- Mute: Indicates the mute function. All mute functions are temporary enabled as long as the world mute option is active.
- Smoke: Indicates a smoke generator function. All smoke functions are temporary disabled as long as the world no smoke option is active.
Momentary duration
TODO
Board
TODO
Tiles
Rail tiles
 Straight
Straight Buffer stop
Buffer stop Tunnel
Tunnel Curve 45°
Curve 45°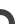 Curve 90°
Curve 90° Crossover 45°
Crossover 45°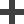 Crossover 90°
Crossover 90° Bridge 45° (left)
Bridge 45° (left)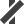 Bridge 45° (right)
Bridge 45° (right)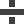 Bridge 90°
Bridge 90°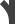 Turnout left 45°
Turnout left 45°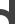 Turnout left 90°
Turnout left 90°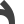 Turnout left curved
Turnout left curved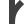 Turnout right 45°
Turnout right 45°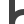 Turnout right 90°
Turnout right 90°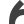 Turnout right curved
Turnout right curved Turnout wye
Turnout wye Turnout 3-way
Turnout 3-way Single slip
Single slip Double slip
Double slip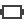 Block
Block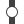 Sensor
Sensor Signal (2 aspects)
Signal (2 aspects) Signal (3 aspects)
Signal (3 aspects)
Clock
TODO
Handheld controllers
TODO
Actions
TODO
Scripting
"Where actions end scripting begins."
Traintastic has a built-in scripting engine, the scripting enginge gives ultimate control over the model world. Using scripting all kind of things can be controled to create an even more realistic world.
Traintastic embeds a Lua scripting engine. Lua is an easy to learn language scripting language for those with or without programmering experiance. Lua is developed by a team at the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio) in Brazil.
To create or edit a script open the Lua scripts list by selecting Objects ➔ Lua scripts from the main menu.
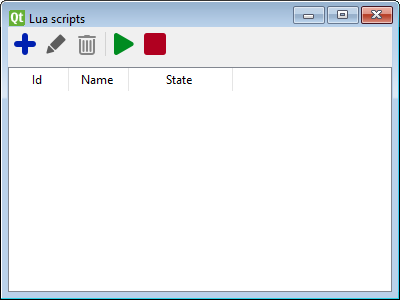
 Create a new script. (Requires edit mode.)
Create a new script. (Requires edit mode.) Edit selected script using the script editor.
Edit selected script using the script editor. Delete selected script. (Requires edit mode.)
Delete selected script. (Requires edit mode.) Run all except disabled scripts.
Run all except disabled scripts. Stop all running scripts.
Stop all running scripts.
Script editor
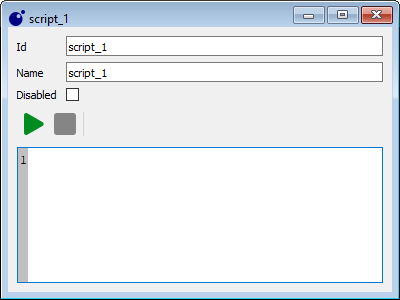
A script can only be edited while it is stopped and edit mode is active. The disabled option can be checked to make sure the script won't run when the run all button is pressed in the Lua script list dialog. If an error occurs during the execution of the script it will be logged in the server log.
See the Lua scripting reference and the Lua scripting examples for more details about Traintastic's scripting possibilities.
For more information about Lua can be found on their website: lua.org
Supported hardware
Traintastic supports hardware of various vendors. This appendix list hardware that is (partly) supported along with instructions and notes how to use it with Traintastic. Product's that aren't listed may still work if they are compatible with a product listed here.
The list is alphabetically ordered by vendor name.
Digikeijs DR5000
TODO
Fleischmann Twin-Center
Fleischmann Z21
See Roco Z21.
Lenz LI100/LI101/LI101F
TODO
Littfinski DatenTechnik HSI-88
TODO
Roco MultiMaus 10764
TODO
Roco Z21
TODO
RoSoft s88xPressNetLI
TODO
Traintastic USB XpressNet interface
TODO
Uhlenbrock IB-COM
The Uhlenbrock IB-COM is a LocoNet command station specifically designed to be used for a computer controlled layout. It can operate up to 32 trains at the same time.
Interface setup
To use the Uhlenbrock IB-COM with Traintastic a LocoNet interface must be created. The Uhlenbrock IB-COM must be connected via USB to the computer running the Traintastic server application.
General settings
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Serial |
| Device | see below |
| Baudrate | 115200 |
| Flow control | Hardware |
On Windows the IB-COM is usually connects as COM3 or COM4, to be sure open the Windows device manager and then connect the USB plug.
On Linux the IB-COM is usually connects as /dev/ttyUSB0, to be sure run dmesg in the console just after connecting the USB plug.
LocoNet settings
From the command station dropdown select Uhlenbrock IB-COM, this will automatically set most LocoNet settings to the best values for the Uhlenbrock IB-COM.
The Uhlenbrock IB-COM does not support LocoNet fast clock, unless there is a fast clock master connected to the LocoNet the Fast clock setting should be Off and the Fast clock sync enabled should be unchecked.
Uhlenbrock Intellibox
TODO
Using the Intellibox serial port
TODO
Using LocoNet
TODO
Uhlenbrock LocoNet interface 63120
TODO
LocoNet
LocoNet is a network bus developed by Digitrax inc. in the early 90's for use with their products. Nowadays LocoNet is used by multiple vendors, products of different vendors can easily be combined due to the standard LocoNet bus. This appendix describes Traintastic's LocoNet implementation details.
Supported LocoNet command stations
The following LocoNet command stations are verified to work with Traintastic:
LocoNet command stations not listed here will probably work but aren't tested.
Supported LocoNet interfaces
The following LocoNet interfaces are verified to work with Traintastic:
- RoSoft LocoNet interface
- Uhlenbrock LocoNet interface 63120
LocoNet interfaces not listed here might work but aren't tested.
Supported LocoNet messages
Traintastic supports most messages defined by Digitrax's LocoNet Personal Use Edition 1.0 specification and some additional messages not covered by the LocoNet Personal Use Edition 1.0 specification, these messages have been retrieved through traffic analysis on the LocoNet network.
Summary of supported LocoNet messages by Traintastic:
- Power control
- Control of locomotive speed and direction
- Control of locomotive functions: F0 … F28
- Reading feedback sensors
- Reading of RailCom feedback
- Reading of LISSY IR sensors
- Control of turnouts, signals and outputs
- Fast clock sync ping
- LNCV programming
Messages defined in the LocoNet Personal Use Edition 1.0 specification:
| Opcode | Supported/Used |
|---|---|
OPC_IDLE |
Yes |
OPC_GPON |
Yes |
OPC_GPOFF |
Yes |
OPC_BUSY |
No |
OPC_SW_ACK |
No |
OPC_SW_STATE |
No |
OPC_RQ_SL_DATA |
Yes |
OPC_MOVE_SLOTS |
No |
OPC_LINK_SLOTS |
No |
OPC_UNLINK_SLOTS |
No |
OPC_CONSIST_FUNC |
No |
OPC_SLOT_STAT1 |
No |
OPC_LONG_ACK |
Partly |
OPC_INPUT_REP |
Yes |
OPC_SW_REP |
No |
OPC_SW_REQ |
Yes |
OPC_LOCO_SND |
Yes |
OPC_LOCO_DIRF |
Yes |
OPC_LOCO_SPD |
Yes |
OPC_WR_SL_DATA |
No |
OPC_SL_RD_DATA |
Yes |
OPC_PEER_XFER |
No |
OPC_IMM_PACKET |
No |
Messages retrieved through traffic analysis:
- Control of locomotive functions: F9 … F28
- RailCOM feedback (
OPC_MULTI_SENSEandOPC_MULTI_SENSE_LONG) - Uhlenbrock LISSY locomotive address, category, direction and speed feedback
- LNCV programming
XpressNet
XpressNet (formally X-Bus) is a network bus developed by Lenz GMBH. This appendix describes Traintastic's XpressNet implementation details.
Supported XpressNet command stations
The following XpressNet command stations are verified to work with Traintastic:
XpressNet command stations not listed here will probably work but aren't tested.
Supported XpressNet interfaces
The following XpressNet interfaces are verified to work with Traintastic:
XpressNet interfaces not listed here might work but aren't tested.
Supported XpressNet messages
TODO
Traintastic DIY protocol
The Traintastic DIY protocol is designed to make it possible to develop custom hardware, e.g. by using the Arduino platform and use it with Traintastic.
The Traintastic DIY protocol is currently supported via:
- Serial port: baudrate and flow control can be chosen, data format is fixed at 8N1 (8 data bits, no parity, one stop bit)
- Network connection (TCP): port number can be chosen.
It is currently limited to:
- Reading inputs
- Controlling outputs
- Throttles
Other features might be added in the future.
Message format
Each Traintastic DIY protocol message starts with an opcode byte, besides the message type it also contains the data payload length in the lowest nibble.
If the lowest nibble is 0xF the the second byte of the message determines the payload length.
The message always ends with a checksum byte, the checksum is the result of XOR-ing of all message bytes.
Examples:
0x50 0x50
The lowest nibble of the first byte is 0 indicating a zero byte payload.
The checksum is identical to the opcode, there is no data to XOR with.
0x24 0x11 0x22 0x33 0x44 0x60
The lowest nibble of the first byte is 4 indicating a 4 byte payload.
The checksum is 0x24 XOR 0x11 XOR 0x22 XOR 0x33 XOR 0x44 = 0x60.
0x2F 0x20 ... 0x??
The lowest nibble of the first byte is F indicating that the second byte must be used as payload length, 32 byte.
The checksum is 0x2F XOR 0x20 XOR all payload bytes.
Messages
Messages are send by Traintastic to the DIY device, for most messages the DIY device sends a response message. Some messages are sent unsolicited by the DIY device to Traintastic if changes are detected by the DIY device.
| Command | |
|---|---|
| Heartbeat | Mandatory |
| Get information | Mandatory |
| Get features | Mandatory |
| Get input state | Mandatory if input feature flag is set |
| Set input state | Mandatory if input feature flag is set |
| Get output state | Mandatory if output feature flag is set |
| Set output state | Mandatory if output feature flag is set |
| Throttle set function | Mandatory if throttle feature flag is set |
| Throttle set speed/direction | Mandatory if throttle feature flag is set |
| Throttle subscribe/unsubscribe | Mandatory if throttle feature flag is set |
Badges:
- The ≥ 0.2 badge indicates in which version of Traintastic the message is added.
Heartbeat ≥ 0.2
The heartbeat message is sent by Traintastic to check if the DIY device is (still) present, the DIY device responds with a heartbeat message. The heartbeat rate can be configured in Traintastic, by default the heartbeat message is one second after the last message is received from the DIY device.
Request message
0x00 <checksum>
Response message
0x00 <checksum>
Get information ≥ 0.2
The get information message is the first message sent after connecting. The DIY device responds with an information message containing a description of the connected DIY device. This is pure informational and displayed in the message console.
Request message
0xF0 <checksum>
Response message
0xFF <len> <text...> <checksum>
Get features ≥ 0.2
The get features message is the second message sent by Traintastic after connecting. The DIY device responds with a features message containing flags which indicate what is supported by the DIY device.
Request message
0xE0 <checksum>
Response message
0xE4 <FF1> <FF2> <FF3> <FF4> <checksum>
<FF1>feature flags 1:- bit 0: input feature flag: set if the DIY device has inputs ≥ 0.2
- bit 1: output feature flag: set if the DIY device has outputs ≥ 0.2
- bit 2: throttle feature flag: set if the DIY device is a throttle ≥ 0.2
- bit 3...7: reserved, must be
0
<FF2>feature flags 2, reserved must be0x00<FF3>feature flags 3, reserved must be0x00<FF4>feature flags 4, reserved must be0x00
Get input state ≥ 0.2
Sent by Traintastic to retrieve the current input state. Address zero has a special meaning, it is used as broadcast address to retrieve the current state of all inputs.
Request message
0x12 <AH> <AL> <checksum>
<AH>high byte of 16bit input address<AL>low byte of 16bit input address
Response
If the address is non zero the DIY device responds with a set input state message containing the current state of the input address.
If the address is zero the DIY device responds with multiple set input state messages, one for each know input address or send a single set input state message with address zero and state invalid to inform Traintastic that the address zero request is not supported.
Set input state ≥ 0.2
Sent by the DIY device as response to the get input state message and must be sent by the DIY device whenever an input state changes.
Message
0x13 <AH> <AL> <S> <checksum>
<AH>high byte of 16bit input address<AL>low byte of 16bit input address<S>input state:0x00if input state is unknown0x01if input state is low/false0x02if input state is high/true0x03if input is invalid (only as response to a get input state message)0x04...0xFFare reserved, do not use
Examples
0x13 0x00 0x12 0x02 0x03
Input 18 state changed to high/true
0x13 0x02 0xA2 0x01 0xB2
Input 674 state changed to low/false
Get output state ≥ 0.2
Sent by Traintastic to retrieve the current output state. Address zero has a special meaning, it is used as broadcast address to retrieve the current state of all outputs.
Request message
0x22 <AH> <AL> <checksum>
<AH>high byte of 16bit output address<AL>low byte of 16bit output address
Response message
If the address is non zero the DIY device responds with a set output state message containing the current state of the output address.
If the address is zero the DIY device responds with multiple set inpoutputut state messages, one for each know output address or send a single set output state message with address zero and state invalid to inform Traintastic that the address zero request is not supported.
Set output state ≥ 0.2
Sent by Traintastic to change the state of an output, the DIY device responds with a get output state message containing the new output state, if for some reason the output state cannot be the current state must be send. Sent by the DIY device as response to the get output state message and must be sent by the DIY device whenever an output state changes.
Message
0x23 <AH> <AL> <S> <checksum>
<AH>high byte of 16bit output address<AL>low byte of 16bit output address<S>output state:0x00if output state is unknown0x01if output state is low/false0x02if output state is high/true0x03if output is invalid (only as response to a get output state message)0x04...0xFFare reserved, do not use
Throttle set speed/direction ≥ 0.2
Set locomotive decoder speed and/or direction.
Once a Throttle set speed/direction message is sent, the throttle id will automatically be subscribed for speed, direction and function changes of the locomotive decoder specified by the decoder address. To stop receiving these changes a throttle unsubscribe message has to be send to Traintastic by the DIY device.
Message
0x37 <TH> <TL> <AH> <AL> <SP> <SM> <FL> <checksum>
<TH>high byte of 16bit throttle id<TL>low byte of 16bit throttle id<AH>:- bit 0...5: highest 6bit of 14bit decoder address
- bit 6 is reserved and must be
0 - bit 7 can be set to force a DCC long address
<AL>lowest 8bit of 14bit decoder address<SP>speed (step),0...<SM><SM>maximum speed (step), set to0for emergency stop<FL>flags:- bit 0: direction
1=forward,0=reverse - bit 1...5: reserved, must be
0 - bit 6: set to set direction
- bit 7: set to set speed
- bit 0: direction
Throttle id can be used to distinguish different throttles within the DIY device if it represents multiple throttles. If the DIY device is a single throttle use 0x00 0x00 as throttle id.
Internally Traintastic uses a value between 0 and 1 for the speed where 0 is stop and 1 is full speed. To determine a value between 0 and 1 Traintastic calculates <SP> / <SM>. Set <SP> and <SM> both to zero for an emergency stop.
Using the flags bit 6 and 7 it is possible to set speed and direction, just the speed, just the direction or nothing. Setting nothing still subscribes the throttle id for speed, direction and function changes.
Examples
0x37 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x03 0x07 0x0E 0xC1 0xFD
Set speed to 50% (= 7 / 14) in forward direction for decoder with address 3.
0x37 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x03 0x00 0x00 0x80 0xB5
Emergency stop decoder with address 3, don't change direction.
Throttle set function ≥ 0.2
Enable/disable locomotive decoder function.
Once a Throttle set function message is sent, the throttle id will automatically be subscribed for speed, direction and function changes of the locomotive decoder specified by the decoder address. To stop receiving these changes a throttle unsubscribe message has to be send to Traintastic by the DIY device.
Message
0x35 <TH> <TL> <AH> <AL> <FN> <checksum>
<TH>high byte of 16bit throttle id<TL>low byte of 16bit throttle id<AH>:- bit 0...5: highest 6bit of 14bit decoder address
- bit 6: reserved and must be
0 - bit 7: set to force a DCC long address
<AL>lowest 8bit of 14bit decoder address<FN>:- bit 0...6: function number
- bit 7: function value
Examples
0x35 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x03 0x80 0xB7
Enable F0 for decoder with address 3.
0x35 0x00 0x02 0x80 0x05 0x01 0xB3
Disable F1 for decoder with long address 5.
Throttle subscribe/unsubscribe ≥ 0.2
Subscribe/unsubscribe for change events. Traintastic will send a throttle set speed/direction message whenever speed or direction changes and a throttle set function message for every function that changes state.
Note Subscribe is supported since ≥ 0.3, older version only support unsubscribe.
Message
0x34 <TH> <TL> <AH> <AL> <checksum>
<TH>high byte of 16bit throttle id<TL>low byte of 16bit throttle id<AH>:- bit 0...5: highest 6bit of 14bit decoder address
- bit 6: action:
0= Unsubscribe,1= Subscribe - bit 7: set to force a DCC long address
<AL>lowest 8bit of 14bit decoder address
When subscribing Traintastic will reply with a throttle set speed/direction and a throttle set function message for every function that is known for the address.
When unsubscribing Traintastic will reply with the same message to confirm the unsubscribe.
Messages
Each log messages has its own unique code, it starts with a letter which indicates the level:
| Letter | Level |
|---|---|
| F | Fatal |
| C | Critical |
| E | Error |
| W | Warning |
| N | Notice |
| I | Info |
| D | Debug |
And a four digit number which indicates the message, the numeric range is divided into different categories for quickly indentifing the source of the message, see below:
| Numbers | Category |
|---|---|
| 1000 … 1999 | Traintastic core components |
| 2000 … 2999 | Hardware interfacing |
| 3000 … 3999 | unused |
| 4000 … 4999 | unused |
| 5000 … 5999 | unused |
| 6000 … 6999 | unused |
| 7000 … 7999 | unused |
| 8000 … 8999 | unused |
| 9000 … 9999 | Lua scripting |
Fatal
TODO
F1001: Opening TCP socket failed (reason)
TODO
F1002: TCP socket address reuse failed (reason)
TODO
F1003: Binding TCP socket failed (reason)
TODO
F1004: TCP socket listen failed (reason)
TODO
F1005: Opening UDP socket failed (reason)
TODO
F1006: UDP socket address reuse failed (reason)
TODO
F1007: Binding udp socket failed (reason)
TODO
F9001: Creating Lua state failed
TODO
F9002: Running script failed (reason)
TODO
F9003: Calling function failed (reason)
TODO
F9999: message
Custom fatal message generated by a Lua script.
Critical
Critical messages indicate that action is required.
C1001: Loading world failed (reason)
TODO
C1002: Creating client failed (reason)
TODO
C1003: Can't write to settings file (reason)
TODO
C1004: Reading world failed (reason) (filename)
TODO
C1005: Saving world failed (reason)
TODO
C1006: Creating world backup failed (reason)
TODO
C1007: Creating world backup directory failed (reason)
TODO
C1008: Creating backup directory failed (reason)
TODO
C1009: Creating settings backup failed (reason)
TODO
C1010: Exporting world failed (reason)
TODO
C1011: Importing world failed (reason)
TODO
C1012: Unknown class 'class id', can't recreate object 'object id'
TODO
C1013: Can't load world saved with newer version, requires at least: Traintastic server version
Cause: The world is saved with a newer version of Traintastic server than currently is running.
Solution: Update Traintastic server (and client) to at least version.
C2001: Address already used at #object
TODO
C2002: DCC++ only supports the DCC protocol
Cause: The selected decoder protocol isn't supported by the DCC++ command station.
Solution: Change the decoder protocol to DCC or Auto.
C2003: DCC++ doesn't support DCC long addresses below 128
Cause: The DCC++ command station considers all addresses below 128 a DCC short address.
Solution: Change the locomotive decoder address.
C2004: Can't get free slot
TODO
C9999: message
Custom critical message generated by a Lua script.
Error
TODO
E1001: Invalid world UUID: uuid
TODO
E1002: World uuid doesn't exist
TODO
E1003: UDP receive error (reason)
TODO
E1004: TCP accept error (reason)
TODO
E1005: Socket shutdown failed (reason)
TODO
E1006: Socket write failed (reason)
TODO
E1007: Socket read failed (reason)
TODO
E1008: Socket acceptor cancel failed (reason)
TODO
E2001: Serial write failed (reason)
TODO
E2002: Serial read failed (reason)
TODO
E2003: Make address failed (reason)
TODO
E2004: Socket open failed (reason)
TODO
E2005: Socket connect failed (reason)
TODO
E2006: Socket bind failed (reason)
TODO
E2007: Socket write failed (reason)
TODO
E2008: Socket read failed (reason)
TODO
E2009: Socket receive failed (reason)
TODO
E2010: Serial port open failed (reason)
TODO
E2011: Socket send failed (reason)
TODO
E2012: Function number already in use
TODO
E2013: Serial port set baudrate failed (reason)
TODO
E2014: Serial port set data bits failed (reason)
TODO
E2015: Serial port set stop bits failed (reason)
TODO
E2016: Serial port set parity failed (reason)
TODO
E2017: Serial port set flow control failed (reason)
TODO
E2018: Timeout, no echo within numberms
TODO
E2019: Timeout, no response within numberms
TODO
E2020: Total number of modules may not exceed number
Cause: The maximum number of S88 modules connected to the HSI-88 may not exceed number, this is a hardware limitation.
Solution: Reduce the number of modules, the sum of left + middle + right must be equal or less than number.
E9001: error (During execution of name event handler)
TODO
E9999: message
Custom error message generated by a Lua script.
Warning
TODO
W1001: Discovery disabled, only allowed on port number
TODO
W1002: Setting name doesnt exist
TODO
W1003: Reading world filename failed (libarchive error code: reason)
TODO
W2001: Received malformed data dropped number bytes
TODO
W2002: Command station doesn't support functions above Fnumber
Cause: The command station or interface can't control these function, e.g. due hardware or protocol limitations.
Solution: Check if command station is setup properly, some command stations have options which specify how to control additional functions. If not, remapping decoder functions or using a different command station is the only solution.
W2003: Command station doesn't support number speed steps, using number
Cause: The command station or interface can't control decoders using number speed steps, e.g. due hardware or protocol limitations.
Solution: The number of speed steps that can be used is determinded by the command station or interface. Changing the decoders speed steps to Auto should usally work.
W2004: Input address address is invalid
The connected Traintastic DIY device does not have an input with address.
W2005: Output address address is invalid
The connected Traintastic DIY device does not have an output with address.
W2006: Command station does not support loco slot slot
Slot slot can't be used with the connected command station, reduce the LocoNet Locomotive slots value.
W2007: Command station does not support the fast clock slot
Fast clock can't be used with the connected command station, disable the LocoNet Fast clock sync enabled setting.
W9999: message
Custom warning message generated by a Lua script.
Notice
TODO
N1001: Received signal: name
TODO
N1002: Created new world
TODO
N1003: Restaring
TODO
N1004: Shutting down
TODO
N1005: Discovery enabled
TODO
N1006: Discovery disabled
TODO
N1007: Listening at address:port
TODO
N1008: Loaded settings
TODO
N1009: Saved settings
TODO
N1010: Edit mode: enabled
TODO
N1011: Edit mode: disabled
TODO
N1012: Communication: enabled
TODO
N1013: Communication: disabled
TODO
N1014: Power: on
TODO
N1015: Power: off
TODO
N1016: Running
TODO
N1017: Stopped
TODO
N1018: Mute: enabled
TODO
N1019: Mute: disabled
TODO
N1020: Smoke: enabled
TODO
N1021: Smoke: disabled
TODO
N1022: Saved world: name
TODO
N1023: Simulation: disabled
TODO
N1024: Simulation: enabled
TODO
N1025: Exported world successfully
TODO
N1026: Imported world successfully
TODO
N2001: Simulation not supported
TODO
N2002: No response from LNCV module id with address address
TODO
N2003: Stopped sending fast clock sync
A fast clock sync message is no longer sent periodically, see W2007.
N9001: Starting script
TODO
N9999: message
Custom notice message generated by a Lua script.
Info
Informational messages
I1001: Traintastic vversion codename
TODO
I1002: Settings file not found, using defaults
TODO
I1003: Client connected
TODO
I1004: Connection lost
TODO
I1005: Building world index
TODO
I1006: boost version
Version information about used boost library, e.g. boost 1.71.0.
I1007: nlohmann::json version
Version information about used nlohmann::json library, e.g. nlohmann::json 3.10.5.
I1008: archive version
Version information about used archive library, e.g. libarchive 3.4.0 zlib/1.2.11 liblzma/5.2.4 bz2lib/1.0.8 liblz4/1.9.2 libzstd/1.4.4.
I2001: Unknown loco address: address
TODO
I2002: Hardware type: type
TODO
I2003: Firmware version: version
TODO
I2004: HSI-88: info
Information about the connected HSI-88 interface, e.g. Ver. 0.62 / 08.07.02 / HSI-88 / (c) LDT.
I2005: info
Information about the connected Traintastic DIY device.
I9001: Stopped script
TODO
I9002: lua version
Version information about used Lua scripting engine, e.g. Lua 5.3.3 Copyright (C) 1994-2016 Lua.org, PUC-Rio.
I9999: message
Custom info message generated by a Lua script.
Debug
TODO
D2001: TX: data
TODO
D2002: RX: data
TODO
D2003: Unknown xHeader 0xvalue
TODO
D2004: source TX: data
TODO
D2005: source RX: data
TODO
D2006: Unknown message: number
TODO
D2007: Input number = value
TODO
D2008: Output number = value
TODO
D2009: Slot number = address
TODO
D2010: Slot number = Free
TODO
D9999: message
Custom debug message generated by a Lua script.
Lua scripting reference
Lua is a scripting language developed at PUC-Rio in Brazil. Lua is a lightweight and easy to learn scripting language especially designed to be embedded in other applications like Traintastic. Lua (pronounced as LOO-ah) means Moon in Portuguese.
Badges:
- The ≥ 0.1 badge indicates in which version of Traintastic it is added.
- The Lua badge indicates it is a standard Lua function.
Globals
TODO
Constants
LUA_VERSION ≥ 0.1
Lua version and copyright, e.g. "Lua 5.3.3 Copyright (C) 1994-2016 Lua.org, PUC-Rio"
VERSION ≥ 0.1
Traintastic version, e.g. "0.1.0-master-380-e669a73b"
VERSION_MAJOR ≥ 0.1
Traintastic major version, e.g. 0
VERSION_MINOR ≥ 0.1
Traintastic minor version, e.g. 1
VERSION_PATCH ≥ 0.1
Traintastic patch level, e.g. 0
Variables
world ≥ 0.1
The global world object.
Functions
assert() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
ipairs() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
next() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
pairs() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
tonumber() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
tostring() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
type() ≥ 0.1
TODO
Libraries
class ≥ 0.1
The class library.
enum ≥ 0.1
The enum library.
log ≥ 0.1
The log library.
math ≥ 0.1
The math library.
set ≥ 0.1
The set library.
string ≥ 0.1
The string library.
table ≥ 0.1
The table library.
Class library
TODO
Constants
class.WORLD ≥ 0.1
TODO
Functions
class.get(object) ≥ 0.1
Returns the class type of object, or nil if object isn't a valid object.
Example
class.get(world) -- returns: class.WORLD
Enum library
TODO
enum.decoder_protocol ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.decoder_protocol.AUTO ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.decoder_protocol.DCC ≥ 0.1
NMRA DCC.
enum.decoder_protocol.MOTOROLA ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.decoder_protocol.SELECTRIX ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.decoder_protocol.CUSTOM ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.direction.FORWARD ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction.REVERSE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction.UNKNOWN ≥ 0.2
TODO
enum.direction_control_state ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.direction_control_state.NONE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction_control_state.A_TO_B ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction_control_state.B_TO_A ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.direction_control_state.BOTH ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.signal_aspect ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.signal_aspect.UNKNOWN ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.signal_aspect.STOP ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.signal_aspect.PROCEED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.signal_aspect.PROCEED_REDUCED_SPEED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.tri_state ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.tri_state.UNDEFINED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.tri_state.FALSE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.tri_state.TRUE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.turnout_position.UNKNOWN ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position.STRAIGHT ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position.LEFT ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position.RIGHT ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position.CROSSED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.turnout_position.DIVERGED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.world_event.EDIT_DISABLED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.EDIT_ENABLED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.OFFLINE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.ONLINE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.POWER_OFF ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.POWER_ON ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.STOP ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.RUN ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.UNMUTE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.MUTE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.NO_SMOKE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.SMOKE ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.SIMULATION_DISABLED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_event.SIMULATION_ENABLED ≥ 0.1
TODO
enum.world_scale ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
enum.world_scale.H0 ≥ 0.1
H0 scale. (1:87)
enum.world_scale.N ≥ 0.1
N scale. (1:160)
enum.world_scale.TT ≥ 0.1
TT scale. (1:120)
enum.world_scale.Z ≥ 0.1
Z scale. (1:220)
enum.world_scale.CUSTOM ≥ 0.1
TODO
Log library
TODO
Functions
debug(...) ≥ 0.1
info(...) ≥ 0.1
notice(...) ≥ 0.1
warning(...) ≥ 0.1
error(...) ≥ 0.1
critical(...) ≥ 0.1
fatal(...) ≥ 0.1
Math library
TODO
Functions
math.abs() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.acos() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.asin() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.atan() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.ceil() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.cos() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.deg() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.exp() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.floor() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.fmod() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.huge() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.log() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.max() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.maxinteger() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.min() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.mininteger() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.modf() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.pi() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.rad() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.random() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.randomseed() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.sin() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.sqrt() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.tan() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.tointeger() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.type() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
math.ult() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
Set library
TODO
set.world_state ≥ 0.1
TODO
Constants
set.world_state.EDIT ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.ONLINE ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.POWER_ON ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.RUN ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.MUTE ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.NO_SMOKE ≥ 0.1
TODO
set.world_state.SIMULATION ≥ 0.1
TODO
String library
TODO
string.byte() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.char() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.find() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.format() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.gmatch() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.gsub() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.len() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.lower() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.match() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.pack() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.packsize() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.rep() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.reverse() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.sub() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.unpack() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
string.upper() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
Table library
TODO
table.concat() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.insert() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.pack() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.unpack() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.remove() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.move() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
table.sort() ≥ 0.1 Lua
TODO
Objects
Board
Properties
id
Object id, unique within the world.
name
Input name.
Methods
None.
Events
None.
Clock ≥ 0.2
The clock object represents the time of the world. There is only one clock object, it can be accessed using world.clock.
Properties
freeze
True if clock is frozen, the clock does not tick.
Note If the clock is not frozen but the world is in Stop state the clock does not tick. To check if the clock is running check running
hour
Hour, 0...23.
minute
Minute, 0...60.
multiplier
Fast clock multiplier rate. That is, one minute in real time represents multiplier minutes of world time.
running
True if clock is running, False if the clock is frozen or the world is in Stop state.
Note The clock only runs if it is not frozen and the world is in Run state.
time
Current time in ticks since midnight, each tick is one fast clock minute.
Methods
None.
Events
on_resume
Fired when the clock resumes.
Handler: function (time, multiplier, clock, user_data)
- time - current time in ticks since midnight, each tick is one fast clock minute;
- multiplier - TODO;
- clock - the clock object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
on_tick
Fired when the clock ticks, once every fast clock minute.
Handler: function (time, clock, user_data)
- time - current time in ticks since midnight, each tick is one fast clock minute;
- clock - the clock object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
on_freeze
Fired when the clock is frozen.
Handler: function (time, clock, user_data)
- time - current time in ticks since midnight, each tick is one fast clock minute;
- clock - the clock object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
Input
Properties
id
Object id, unique within the world.
name
Input name.
value
Input value, an enum.tristate value.
Note The input value can be enum.tristate.UNDEFINED, especially when just connected to the hardware.
Methods
None.
Events
on_value_changed
Fired when the input value changes.
Handler: function (value, input, user_data)
- value -
trueif the input value changed to high,falseif the input value changed to low; - input - the input object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
Example: Direction control using an input.
Output
Properties
id
Object id, unique within the world.
name
Output name.
value
Output value, an enum.tristate value.
Note The output value can be enum.tristate.UNDEFINED, especially when just connected to the hardware.
Methods
set_value(value)
Set the output value to true or false. The method returns true if the command was succesfully sent to the hardware, false otherwise.
Note Reading value after calling set_value() may still return the old value, value is updated after the hardware comfirmed the newly set value.
Events
on_value_changed
Fired when the output value changes.
Handler: function (value, output, user_data)
- value -
trueif the output value changed to high,falseif the output value changed to low; - output - the output object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
List
TODO
World
Properties
boards ≥ 0.1
List of all boards.
clock ≥ 0.2
The world clock, see Clock.
name ≥ 0.1
World name.
rail_vehicles ≥ 0.1
List of all rail vehicles.
scale ≥ 0.1
World scale, an enum.world_scale value.
scale_ratio ≥ 0.1
World scale ratio in 1:value, e.g. for H0 it returns 87.
state ≥ 0.1
World state, a set.world_state value.
trains ≥ 0.1
List of all trains.
uuid ≥ 0.1
World UUID (Universal Unique Identifier), every world that is created has its own unique UUID.
Methods
get_object(id) ≥ 0.1
Get object with id, if it exists it returns the object, else it returns nil.
power_off() ≥ 0.1
Stop all vehicles and power off, identical to pressing power off in the Traintastic client application.
stop() ≥ 0.1
Stop all vehicles, identical to pressing stop in the Traintastic client application.
Events
on_event ≥ 0.1
Fired when the world state changes,
e.g. when pressing the stop button in the Traintastic client application or calling world.stop().
Handler: function (state, event, world, user_data)
- state - a
set.world_statevalue; - event - an
enum.world_eventvalue; - world - the world object;
- user_data - user data that was set or
nilif no user data was set during connect.
Example: Control output on world run/stop.
Lua scripting examples
TODO
Badges:
- The ≥ 0.1 badge indicates in which version of Traintastic is minimal required for the example to work.
Control output on world run/stop ≥ 0.2
This examples monitors the world state and controls an output based on the run flag. If the world in in run state the output is off, if the world is stopped the output is on, e.g. for controller a red lamp.
-- world event handler
function world_event(state)
-- get the output to control
local output = world.get_object('output_1')
-- check if the RUN flag is set in the world state
if world.state.contains(set.world_state.RUN) then
-- turn output off
output.set_value(false)
else
-- turn output on
output.set_value(true)
end
end
-- register the event handler
world.on_event = world_event
-- call event handler once at script start to set output to current world state
world_event(world.state)
The event handler above is a bit verbose for clarity, it can also be written more compact as:
function world_event(state)
world.get_object('output_1').set_value(not world.state.contains(set.world_state.RUN))
end
Direction control using an input ≥ 0.1
This example show how to use an input to control a direction control board element on the board. This can e.g. be used for physical control panels that control board elements.
world.get_object('input_1').on_value_changed(
function (value)
-- get the direction tile to control
local direction_control = world.get_object('direction_1')
-- state state based on input value
if value then
direction_control.set_state(enum.direction_control_state.B_TO_A)
else
direction_control.set_state(enum.direction_control_state.A_TO_B)
end
end)
Command line options
The client and server both support various command line options to contol how the applications start and where data is stored. These options are mainly useful for PCs only used to control the layout.
Traintastic client
| Short | Long | Description |
|---|---|---|
-h |
--help |
Displays help text. |
-v |
--version |
Displays version information. |
--fullscreen |
Start application fullscreen. | |
-c <hostname[:port]> |
--connect <hostname[:port]> |
Connect to server. |
Traintastic server
Command line options available for Traintastic server depend on the used operation system.
Generic
Traintastic server command line options available on all supported operating systems:
| Short | Long | Description |
|---|---|---|
-h |
--help |
Display help text and exit |
-v |
--version |
Output version information and exit |
-D PATH |
--datadir PATH |
Data directory |
-W UUID |
--world UUID |
World UUID to load |
--simulate |
Enable simulation after loading world | |
--online |
Enable communication after loading world | |
--power |
Enable power after loading world | |
--run |
Start after loading world |
Note --simulate, --online, --power and --run options only apply to the world loaded at startup.
Note --run option requires --power, --power option must be set for --run to work.
Data directory
The data directory is the location where Traintastic server stores all its data, such as: settings, worlds, logfile, backups. The default location differs per operating system:
- Windows:
%LOCALAPPDATA%\traintastic\server, e.g.C:\Users\reinder\AppData\Local\traintastic\server - Linux:
~/.config/traintastic-server, e.g./home/reinder/.config/traintastic-server
Note Traintastic server stores its data per user. To use the same settings, worlds, logfile, backups with multiple user accounts they all must start Traintastic server with the data directory option pointing to a location that is writable by all involved user accounts.
Windows
Traintastic server command line options only available for Windows:
| Short | Long | Description |
|---|---|---|
--tray |
Run application in system tray |
Linux and macOS
Traintastic server command line options only available for Linux and macOS:
| Short | Long | Description |
|---|---|---|
-d |
--daemonize |
Daemonize |
-u USERNAME |
--user USERNAME |
Run as user |
-g GROUPNAME |
--group GROUPNAME |
Run as group |
-p [FILENAME] |
--pidfile [FILENAME] |
Write pid file, FILENAME defaults to /run/traintastic-server.pid |
